WireGuard vs OpenVPN: Which Protocol Should You Use?
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) rely on VPN protocols to make connections and secure your online traffic over the internet. At the moment, WireGuard and OpenVPN are regarded as the best protocols in the VPN industry.
This comparison guide looks at WireGuard and OpenVPN in key aspects like security, privacy, speeds, and ease of use. It also highlights their features, benefits, and a little background information.
Keep on reading to learn more about how the two VPN protocols compare with each other! Learn which one is the best VPN protocol.
When it comes to VPN protocols, WireGuard and OpenVPN are both highly esteemed for their unique strengths and features.
OpenVPN: A Veteran in the Industry
Launched in 2001, OpenVPN has long been a favorite in the VPN industry. It is renowned for its robust privacy and security features, making it a reliable choice for many users. Its longevity and widespread adoption are a testament to its effectiveness.
WireGuard: The New Contender
Introduced in 2019, WireGuard has rapidly gained popularity due to its impressive speed and dependable security. Its newer design incorporates modern technologies, which contribute to its superior performance and efficiency.
Common Ground
Both WireGuard and OpenVPN are open-source protocols, enhancing their transparency and trustworthiness. Many leading VPN providers support both, ensuring users have access to reliable and secure VPN services.
Strengths of WireGuard
- Fast connection speeds
- Minimal bandwidth usage
- Efficient network switching
- Smaller code base, simplifying security audits and reducing vulnerabilities
Strengths of OpenVPN
- High-security standards
- Effective in navigating censored regions
- Uses a diverse range of encryption methods
- Backed by a large, committed community
Choosing between WireGuard and OpenVPN depends on your specific needs and priorities. WireGuard offers rapid speeds and efficiency, while OpenVPN provides established security and flexibility. Each protocol has its own set of unique advantages, making both valuable options in the realm of VPN technology.
WireGuard vs OpenVPN: Quick Summary
OpenVPN entered the market in 2001 and has since been regarded as the industry standard regarding privacy and security.
However, WireGuard, a 2019 addition, has taken over the commercial VPN industry thanks to its fast speeds and relatively impressive security standards.
Both WireGuard and OpenVPN are open source, and some of the best VPN providers, such as NordVPN, Surfshark, Private Internet Access and CyberGhost offer the protocols in their VPN apps.
Some VPN providers have created proprietary protocols based on WireGuard VPN or OpenVPN code.
WireGuard’s primary goals are to improve the existing VPN protocols with simplicity, speed, ease of use, and reduced scope of the attack surface – it uses state-of-the-art cryptography.
Thus, it offers a solution for every VPN (Virtual Private Network) aspect.
OpenVPN uses multiple VPN encryption techniques, and it has over 60 million downloads. Being in the industry for so long, OpenVPN is virtually used by every VPN client in the market, both commercial and corporate.
Even with the emergence of new protocols and stiff competition, OpenVPN continues to be the center stage of VPN security.
Even with differences between the two protocols, they share the goal of being fast, secure, stable, and reliable.
Feature Highlights
WireGuard protocol is best known for:
- Super-fast connection speeds.
- Allows multiple switches between networks.
- Let’s you manually set up a VPN network on your own.
- Consumes less bandwidth.
OpenVPN is best known for:
- Accessing heavily censored regions like China, Russia, and more.
- Best-in-class security protocol.
- Uses the vast OpenSSL library for cryptography.
- Thoroughly tested and has stood the test of time.
Here is a brief comparison of the features to get you started:
| Features | WireGuard | OpenVPN |
| Date Released | September 2019 | May 2001 |
| Code Size | ≈ 4,000 lines | More than 70,000 lines |
| Commonly used Ciphers | ChaCha20, Poly1305 | AES, Blowfish, Camellia |
| Perfect Forward Secrecy | Yes | Yes |
| Security | Strong | Strong |
| Stability | Stable | Stable |
| Privacy | Strong | Requires Mitigation |
| Bypass Censorship | Barely | Yes |
| Speeds and performance | Very fast | Balanced |
| Open Source | Yes | Yes |
| Compatibility | Gaining adoption | Natively supported |
Code size
WireGuard comprises around 4,000 lines of code. OpenVPN, on the other hand, has over 70,000 lines.
Furthermore, the modified versions of OpenVPN are known to reach up to 600,000 lines of code.
By using fewer lines of code, WireGuard reduces the attack surface and hence fewer chances of a possible cyber-attack.
With a smaller code base, developers can identify vulnerabilities easily, and a single auditor can quickly audit the code. Thus, hackers are less likely to identify security flaws in WireGuard.
Even with a massive codebase, OpenVPN is not vulnerable to attacks. Maybe it was susceptible in the earlier days.
One of the perks of being in the industry for almost two decades is thorough scrutiny.
Additionally, OpenVPN has a large community with various stakeholders, ensuring it is always bugless.
Auditability
Both WireGuard and OpenVPN are open-source. This makes it easy for anyone to access and audit the source code and other aspects.
Due to WireGuards’ less bulky code, as compared to OpenVPN’s code, WireGuard can be quickly audited. However, even with the less bulky code, WireGuard has not earned the trust of security auditors.
Unlike WireGuard, OpenVPN has stood the test of time and undergone several audits.
Even with more than 70,000 lines of code and a requirement of a larger team, OpenVPN is a well-audited protocol, and various security experts acknowledge it well.
This is because it has existed, and most VPN tunnel connections rely on it.
Nonetheless, WireGuard is catching up; this protocol will get the same attention as OpenVPN after mass adoption.
With less bulky code, it can be audited several times more than OpenVPN in a short period.
Security and Encryption
WireGuard and OpenVPN support a range of secure encryption techniques and encryption algorithms, especially ciphers.
However, even with state-of-the-art cryptography, WireGuard is not agile compared to OpenVPN. WireGuard has a fixed set of encryption techniques for a specific software release.
If a bug or a security vulnerability is found within the set, the next update addresses the vulnerability with another set of symmetric encryption techniques and cryptographic algorithms.
But this is bound to change. For OpenVPN, you can quickly switch to the encryption that works. This also accounts for why WireGuard is less bulky than OpenVPN.
Commonly used ciphers and encryption techniques for WireGuard include ChaCha20 and Poly1305. ChaCha20 is used for encryptions, while Poly1305 is used for authentications.
It can also use other cryptography techniques such as Noise protocol framework, Curve25519, BLAKE2, SipHash24, and HKDF.
On the other hand, OpenVPN commonly uses AES, Blowfish, and Camellia. Additionally, since OpenVPN relies on the OpenSSL library, it can use other cryptography techniques such as Chacha20, Poly1305, SEED, CAST-128, DES, SHA-2, SHA-3, BLAKE2, RSA, DSA, Diffie–Hellman key exchange, Elliptic curve, among many others.
OpenVPN uses the most tested encryption techniques, which are more reliable, unlike WireGuard’s newer algorithms. The technology is 18 years older and uses a decade-old AES cipher.
WireGuard uses much newer techniques like ChaCha20 and Poly1035.
Nonetheless, the argument changes when you put the two protocols into practice. For instance, WireGuard’s much newer encryption technology poses little to no security threat, and here’s why:
- ChaCha20 is highly secure because it has evolved over time and now has over 20 levels of security.
- Less time is required to audit WireGuard, thanks to its minimal code size.
- Recognition from tech giants like Google and the more secure Operating System, Linux.
Crypto-Agility vs. The Attack Surface
Crypto-agility is a security system’s ability to automatically switch between algorithms, protocols, and other encryption techniques.
WireGuard doesn’t have crypto-agility since it uses a fixed set of a single cryptographic suite for each version. This crypto-agility trade-off reduces attacks’ complexity and vulnerabilities, including the man-in-the-middle attack.
Thus, this makes it more secure from the attack perspective but not the protection perspective.
On the other hand, OpenVPN is a crypto-agile protocol; it can use multiple cryptographic suites, resulting in more robust protection.
But again, with more suites, you get more complexity, increasing the attack surface and downgrade attacks. On the bright side, OpenVPN won’t force you to upgrade like WireGuard when an attack occurs.
WireGuard uses a system called ‘Versioning’ to change the cryptographic suites in case of a vulnerability. This WireGuard system prompts servers to request connections over the new version and ignore the old package.
Thanks to this, WireGuard has avoided being a victim of regular non-crypto-agile systems attacks.
Privacy and Logging
If you’re keen on privacy, settling on a VPN service with a zero logs policy that guarantees absolute privacy is crucial. This should also apply to the VPN protocol the service uses.
OpenVPN has a complete zero logs policy. But this isn’t the case with WireGuard, which is designed to store permitted IP addresses until the next server reboot.
In this regard, WireGuard poses a security risk. This is because if a VPN server is compromised, all IP addresses stored in it will be used to link back to your online activity.
Your IP address will likely be logged if you’re using a standard WireGuard protocol. This is why some VPN solution providers are creating proprietary protocols based on WireGuard to mitigate this privacy issue.
Other building upon WireGuard, there’s a workaround that other top Android VPNs use to mitigate this privacy risk. Here are some of the tricks used:
- Using double Network Address Translation (NAT): This NAT assigns you a dynamic IP address to every VPN connection you make. This implies that every session has a unique IP address that only works until you disconnect from a VPN server.
- Using a multihop (double VPN) feature: This feature routes your online traffic via multiple servers using WireGuard. This technique also deletes your IP address from the server after a certain period of inactivity.
Additionally, if you’re concerned about privacy, you must confirm with your VPN provider the mitigation solutions they have for WireGuard.
Overcoming Censorship
OpenVPN excels at overcoming internet censorship because it can use TCP instead of UDP with port 433, which is also used by HTTPS.
This trick makes it hard for all firewalls to differentiate between OpenVPN traffic and normal, secure web traffic.
Thanks to this trick, OpenVPN is very efficient in highly censored countries like China, Russia, and Turkey.
Under normal circumstances, we recommend using UDP for improved speeds, but TCP is a much safer bet if you want to bypass highly censored regions.
The only trade-off, TCP is much slower than UDP but highly reliable.
WireGuard barely bypasses censorship and is susceptible to Deep Packet inspection. This is because of WireGuard trades-off obfuscation for speed. Thus, WireGuard does not support tunneling over TCP.
Its UDP connections are easily spotted and blocked by various censorship techniques.
WireGuard is not that great for unblocking websites.
Network Switching Mobility
Generally, when it comes to network mobility, the IKEv2 protocol is preferred by many VPN providers since it supports the Mobility and Multihoming Protocol.
However, there are concerns regarding the protocol’s closed source approach. Also, IKEv2 is offered out-of-the-box by many mobile devices; hence you can configure your VPN connection.
In comparison between WireGuard and OpenVPN, WireGuard offers better mobility.
With WireGuard, you can seamlessly switch between Wi-Fi and mobile networks, better than OpenVPN.
Many internet users tend to disconnect and reconnect OpenVPN when they switch networks and thus have connection drops.
If you’re constantly switching networks, it is recommendable to use a VPN that supports WireGuard for an improved internet experience.
Therefore, WireGuard offers an excellent solution to both IKEv2 and OpenVPN problems; it is an open-source solution and eliminates the OpenVPN mobility issue.
Bandwidth Usage, Performance, and Speed
WireGuard uses less bandwidth than OpenVPN. WireGuard uses fewer encryption techniques than its competitor, hence a low encryption overhead.
Therefore, encryption time is fast and requires fewer data to achieve security when using a VPN.
Less encryption overhead is essential when you are using pay-as-you-go mobile bandwidth. With OpenVPN, you will use more data due to its huge encryption overhead during tunneling.
Regarding speed and performance, WireGuard is faster as it mainly relies on UDP connections.
Additionally, it uses fewer CPU resources in mobile devices, embedded systems, and routers because it lives inside the Linux kernel. Additionally, WireGuard also establishes connections quickly.
On the other hand, Open VPN is fast but not as WireGuard when using UDP. However, when you opt for reliability and bypassing restrictions, you will get slower speeds since you must use the TCP connection.
TCP connection prioritizes reliability over speed.
Also, since OpenVPN has a higher encryption overhead, it uses more CPU resources, which can be problematic to devices that don’t have high-performance CPUs, such as routers and embedded systems.
You will also realize battery drainage due to high CPU usage.
Additionally, performance-wise, OpenVPN has never been the best option since even other outdated protocols yield better results.
The WireGuard uses multi-threading better in modern CPUs, which OpenVPN hasn’t utilized fully.
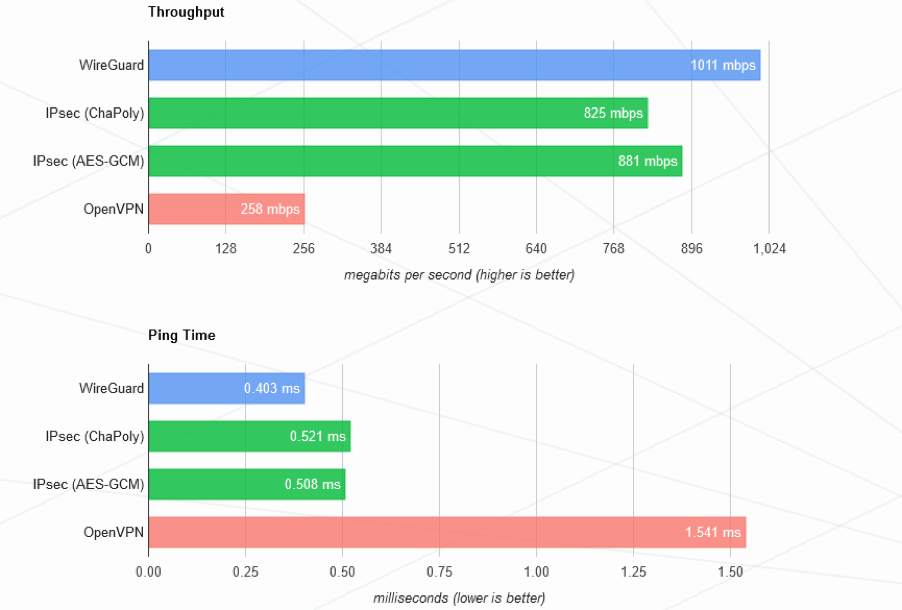
WireGuard conducted a high-performance benchmark with the same parameters on IPSec, WireGuard, and OpenVPN protocol.
Here are the results:
From the above chart, WireGuard has better throughput and lower ping time than its counterpart.
You can also conduct speed tests to confirm which protocol yields excellent speeds.
Close all programs and launch a VPN that supports WireGuard, maybe Surfshark or NordVPN.
Connect to various servers and measure the speeds using Speedtest by ookla. You can use open VPN UDP and TCP against WireGuard.
Compatibility and Ease of Use
Virtually every VPN in the industry uses OpenVPN. You can also get OpenVPN on most routers, consoles, and other devices.
However, WireGuard doesn’t enjoy this popularity yet, but it’ll soon have a similar presence to OpenVPN with mass adoption.
Due to the lean code, it is easy for developers to tweak WireGuard to work or support more devices, excluding legacy systems that won’t support new protocols. Additionally, WireGuard has excellent usability and cross-platform support.
Most VPNs still use the OpenVPN protocol on the router level. But you’ll be pleased to know that a select few VPNs now allow you to use WireGuard at the router level.
On mobile devices, most popular VPNs offer the WireGuard protocol.
Regarding ease of use, WireGuard is straightforward as compared to OpenVPN. This can also be attributed to its less bulky codebase, making it a better option for embedded systems.
OpenVPN has been and is still hard to configure manually. Nonetheless, the process is more straightforward with a third-party client.
Wrap Up
WireGuard is a recent entry into the industry but has already created a name for itself. This is evident in the number of top VPNs incorporating the protocol in their service.
The best part is that WireGuard is now available in the Linux kernel.
OpenVPN is a much older and more respectable protocol in the industry. This is always going to command trust and more loyalty to technical users.
However, there’s no denying how fast WireGuard matches and arguably does better than OpenVPN in various aspects, including speed, codebase, performance, and usability.
Concisely, WireGuard and OpenVPN protocols are pretty matched in this head-to-head comparison. Thus, it’s not easy deciding on the better of the two VPN protocols.
To determine which protocol you should use, you must decide what aspect to trade off. Nonetheless, both protocols are great for day-to-day use.
Frequently Asked Questions
Some people found answers to these questions helpful
Can WireGuard replace OpenVPN?
WireGuard strives to replace the IPSec protocol suite in terms of features and benefits. It also aims to match OpenVPN, but it’s still falling short regarding security levels and compatibility. WireGuard is still a new protocol, and its features are attracting more users.
Is WireGuard Safe in 2022?
WireGuard is considered highly secure, but it doesn’t suit privacy-oriented users. For instance, WireGuard doesn’t entirely observe a no-logs policy as it stores most user IP addresses. This practice means that hackers can quickly get a sniff of your online activity without your consent.
Is WireGuard the fastest VPN protocol?
Yes, arguably, WireGuard is currently the fastest VPN protocol in the market. WireGuard works within the Linux kernel and uses primitive cryptography. This trick makes the VPN protocol very fast while exhibiting decent security standards.
How faster is WireGuard than OpenVPN?
On average, WireGuard is about 50% faster than OpenVPN. The protocol’s speed performance over OpenVPN increases when you connect to nearby (low-latency) server locations and slightly reduces over far away (high-latency) servers.
Is WireGuard less secure than OpenVPN?
Yes, WireGuard is less secure than OpenVPN, but that doesn’t make it vulnerable to attacks. On the other hand, OpenVPN is considered the industry standard in terms of security. OpenVPN is also much older and has been thoroughly audited over time.



3 Comments
99 CLUB
June 10, 2025 9:24 am
Great comparison! I’ve been using OpenVPN for a while, but the simplicity and speed of WireGuard seem really appealing. I appreciate the detailed breakdown of the pros and cons—definitely helps in making an informed choice!
19 Club login
June 2, 2025 8:43 pm
Great comparison! I’ve been using OpenVPN for a while, but I’m really intrigued by WireGuard’s performance and simplicity. I appreciate the insights you’ve provided; they helped clarify my thoughts on switching protocols.
Dg Club Login
May 19, 2025 5:08 pm
Great comparison! I’ve been considering switching to WireGuard for its speed and simplicity. However, I appreciate the detailed look at OpenVPN’s proven security features. It’s a tough choice, but this post helped clarify some of the differences. Thanks for the insights!